Orthodontic treatment aims to achieve precise tooth movement, restoring both function and aesthetics. To accomplish this, various types of springs play a crucial role by controlling torque, axial movement, and space adjustment. In this article, we will explore the torque spring, nickel-titanium coil spring, T-loop archwire, and nickel-titanium push spring, focusing on their functions, material properties, and clinical applications.
1. Orthodontic Torque Spring
Function
The orthodontic torque spring helps control tooth torque, adjusting the inclination of the tooth along its long axis. This adjustment ensures an ideal position for both the root and the crown. Clinicians often use this spring in the following situations:
- Deep bite correction: Patients with a deep bite frequently require anterior teeth repositioning. The torque spring provides stable torsional force, helping correct the inclination effectively.
- Protrusion correction: In maxillary protrusion cases, the torque spring assists in adjusting the lingual inclination of the anterior teeth, which significantly improves the overall treatment outcome.
Material and Mechanical Properties
- Stainless steel or nickel-titanium alloy: These materials offer high elasticity, ensuring sustained and stable force throughout treatment.
- Compatibility with rectangular archwires: This feature enhances torque control, allowing coordinated movement of both the root and crown.

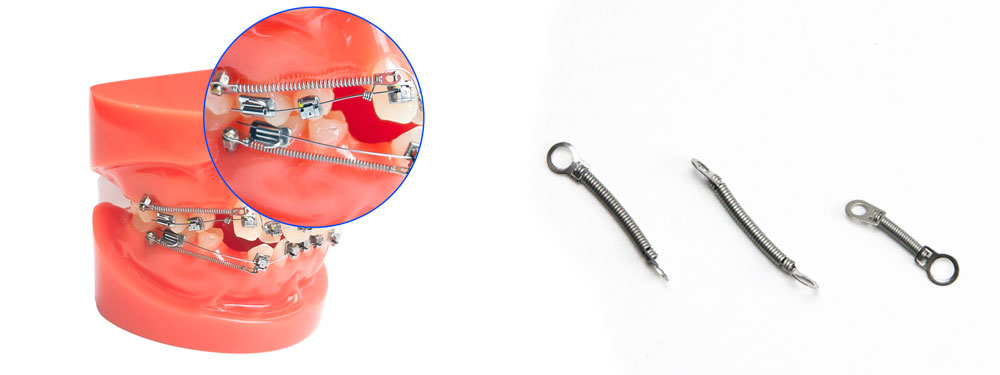
2. Orthodontic Nickel-Titanium Coil Spring
Function
Nickel-titanium coil springs primarily adjust space in orthodontic treatment. They either close extraction spaces or create gaps by pushing teeth apart. Orthodontists often rely on these springs in the following cases:
- Extraction cases: After a tooth is removed, the coil spring applies a steady force to shift neighboring teeth into the empty space.
- Crowding correction: When the dental arch lacks sufficient space, an open coil spring pushes adjacent teeth apart, creating room for alignment.
Material and Mechanical Properties
- Nickel-titanium alloy (Ni-Ti): Due to its superelasticity and shape memory properties, this material provides a consistent force, reducing the need for frequent adjustments.
- Low friction: Compared to traditional stainless steel coil springs, Ni-Ti coil springs minimize friction, which helps lower the risk of root resorption and enhances treatment efficiency.
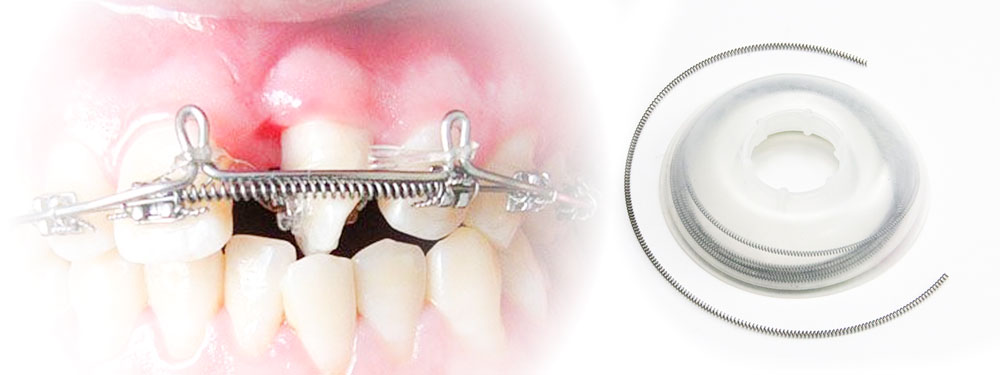
3. Orthodontic T-Loop Archwire
Function
The T-loop archwire is a functional wire structure that facilitates anterior retraction and extraction space closure. By distributing orthodontic forces effectively, it prevents undesirable tooth tipping. Some common applications include:
- Extraction space closure: The T-loop archwire carefully directs root movement while closing spaces, ensuring proper alignment without excessive crown tipping.
- Arch form adjustment: When orthodontists need to modify the dental arch shape, the T-loop provides reliable force application.
Material and Mechanical Properties
- Titanium-molybdenum alloy (TMA) or stainless steel: These materials offer both strength and elasticity, allowing precise control of orthodontic forces.
- Adjustability: By modifying bending angles and loop configurations, orthodontists can fine-tune tooth movement based on patient needs.

4. Orthodontic Nickel-Titanium Push Spring
Function
The nickel-titanium push spring primarily distalizes teeth, making it valuable for correcting crowding, expanding the dental arch, and creating space for implants. This spring proves particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Arch expansion: In patients with a narrow maxilla, the push spring continuously exerts force, moving teeth distally to create a wider dental arch.
- Mild anterior protrusion correction: When slight repositioning of anterior teeth is necessary, the push spring applies gentle force, reducing patient discomfort while achieving gradual movement.
Material and Mechanical Properties
- Nickel-titanium alloy: With high fatigue resistance, this material ensures consistent force application throughout treatment.
- Sustained force delivery: Unlike traditional stainless steel push springs, Ni-Ti push springs maintain a steady force over time, reducing the need for frequent orthodontic adjustments.
References
- American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, 2021. “Effect of Nickel-Titanium Coil Springs on Tooth Movement and Root Resorption.”
- European Journal of Orthodontics, 2020. “Comparative Study of Stainless Steel and Nickel-Titanium Orthodontic Springs.”
- The Angle Orthodontist, 2019. “Biomechanical Analysis of T-loop Archwire in Space Closure.”
- Journal of Clinical Orthodontics, 2021. “Clinical Efficiency of Nickel-Titanium Push Springs in Anterior Segment Retraction.”

Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
Hello hengshengspring.com Owner.