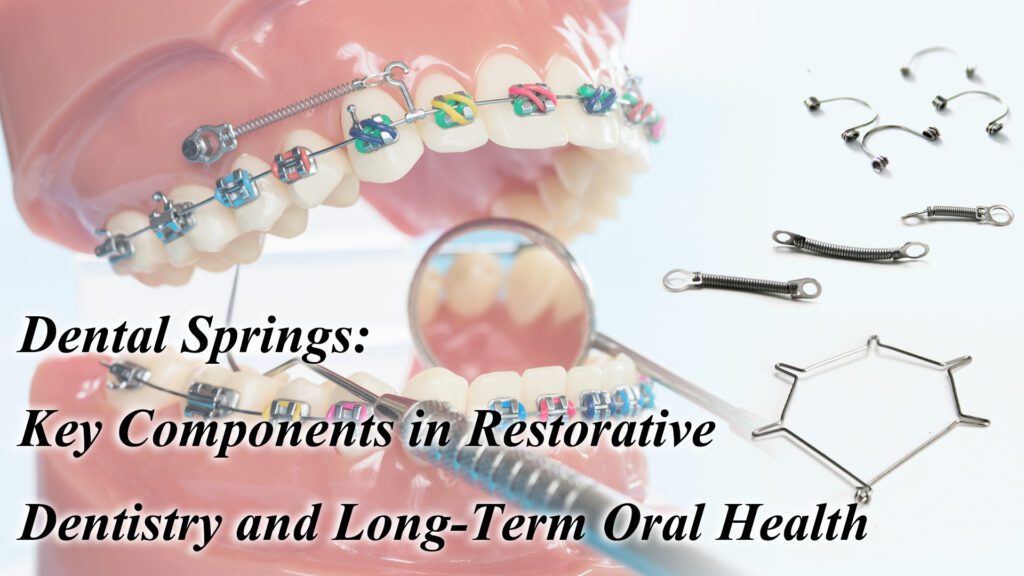
In modern dentistry, even the smallest components play a crucial role in treatment success. Dental springs, though small, are indispensable for ensuring comfort, precision, and long-term functionality in dental appliances, especially in orthodontics and prosthetics. These components are responsible for adjusting, stabilizing, and retaining dental structures, making them essential in daily dental treatments.
This article will explore the various types of dental springs, the materials used, their benefits, and recent advancements in dental spring technology. By understanding these aspects, dental professionals can make informed decisions to ensure the best outcomes for their patients.
What Are Dental Springs?
Dental springs are mechanical devices that apply controlled force on teeth or dentures. These springs are commonly used in orthodontic appliances like braces and retainers, as well as in dentures to improve retention and comfort. Materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and nickel-titanium alloys are chosen for their durability, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in the mouth.
Dental springs apply precise amounts of force, allowing for gradual and controlled adjustments in orthodontic and denture treatments.
Types of Dental Springs
Dental springs come in several forms, each designed for specific dental applications. The most commonly used types include:
1. Orthodontic Springs
Orthodontic springs are used to apply force to shift teeth into proper alignment. Common types include:
- Coil Springs: These springs create space between teeth and gradually shift them into position.
- Torsion Springs: These apply rotational force to adjust the angle of a tooth.
- Compression Springs: These springs apply compressive force to move teeth into alignment.
2. Retention Springs
After teeth are aligned, retention springs keep them in place during the stabilization process. These springs are often used in retainers to ensure teeth do not shift back to their original position. Retention springs are typically less visible than orthodontic springs, offering a more comfortable fit for patients.
3. Springs for Dentures
Springs also enhance the comfort and stability of dentures. For example:
- Snap-on Retainers: These retainers use springs to secure removable dentures in place.
- Clasp Springs: These springs ensure partial dentures fit comfortably and securely.
Materials Used in Dental Springs
Choosing the right material for dental springs is crucial for ensuring strength, comfort, and resistance to wear. Below are the most commonly used materials:
1. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is the most widely used material for orthodontic springs. It is strong, flexible, and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for springs that must endure the forces of orthodontic treatment.
2. Titanium
Titanium is often preferred for patients with sensitivities to other metals. It is lightweight, highly biocompatible, and corrosion-resistant. Titanium springs are used in various dental applications, offering increased comfort for long-term wear.
3. Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Alloys
Nickel-titanium alloys provide superelasticity, which allows the springs to return to their original shape after substantial deformation. This property makes NiTi alloys ideal for orthodontic springs that need to apply consistent force over time.
Why Dental Springs Matter
Dental springs are essential to the success of orthodontic treatments and prosthetics. Here’s why they are so important:
- Precision and Control: Dental springs apply specific amounts of force, crucial for effective orthodontic treatment. They move teeth gradually without causing discomfort.
- Comfort and Adaptability: Well-designed springs ensure a smooth and comfortable treatment process for patients.
- Durability and Longevity: Dental springs are designed to withstand the harsh conditions inside the mouth, remaining effective over time.
- Customization: Dental springs can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each patient, whether for tooth alignment, retention, or denture stabilization.
Recent Advances and Research in Dental Springs
Recent research highlights significant improvements in dental spring technology. A study published in The Journal of Clinical Orthodontics concluded that nickel-titanium springs outperform stainless steel ones due to their ability to apply more consistent forces, leading to better patient outcomes (Sato et al., 2023).
Another study in The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry focused on titanium springs used in dentures. Researchers found that titanium’s biocompatibility reduces irritation, making it the ideal choice for patients with sensitive mouths (Kobayashi & Tanaka, 2022).
These advancements underscore the importance of selecting the right materials and designs to meet each patient’s unique needs. As dental technology continues to evolve, dental springs will become even more efficient, comfortable, and durable.
Choosing the Right Dental Spring
Selecting the appropriate dental spring involves considering the following factors:
- Treatment Objective: The type of spring will depend on whether the goal is to align teeth, retain them after treatment, or stabilize dentures.
- Patient Comfort: The spring must apply force gradually to avoid discomfort during treatment.
- Material Durability: Choose materials that are strong, resistant to wear, and suitable for long-term use.
By carefully considering these factors, dental professionals can select the most suitable spring for each patient’s needs, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
Dental springs are integral to the effectiveness of modern orthodontic treatments and dentures. They help apply controlled force, align teeth, and stabilize dentures for improved comfort and function. By selecting the right material and design, dental professionals can ensure that treatments are effective and long-lasting.
If you’re unsure about which type of spring is best for your treatment, consult with a dental professional. With a better understanding of dental springs, patients and practitioners can work together to achieve the best possible results.
- Sato, T., et al. (2023). Advantages of Nickel-Titanium Springs in Orthodontic Treatment. The Journal of Clinical Orthodontics, 57(6), 110-115.
- Kobayashi, K., & Tanaka, Y. (2022). Titanium Springs for Partial Dentures: Biocompatibility and Effectiveness. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 129(4), 251-257.