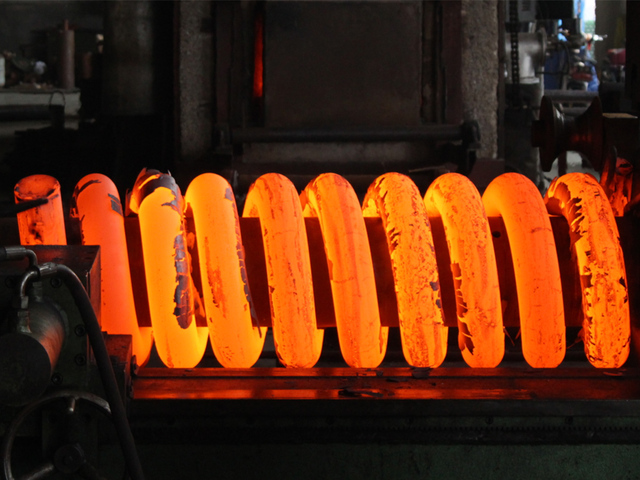
Hot coil spring
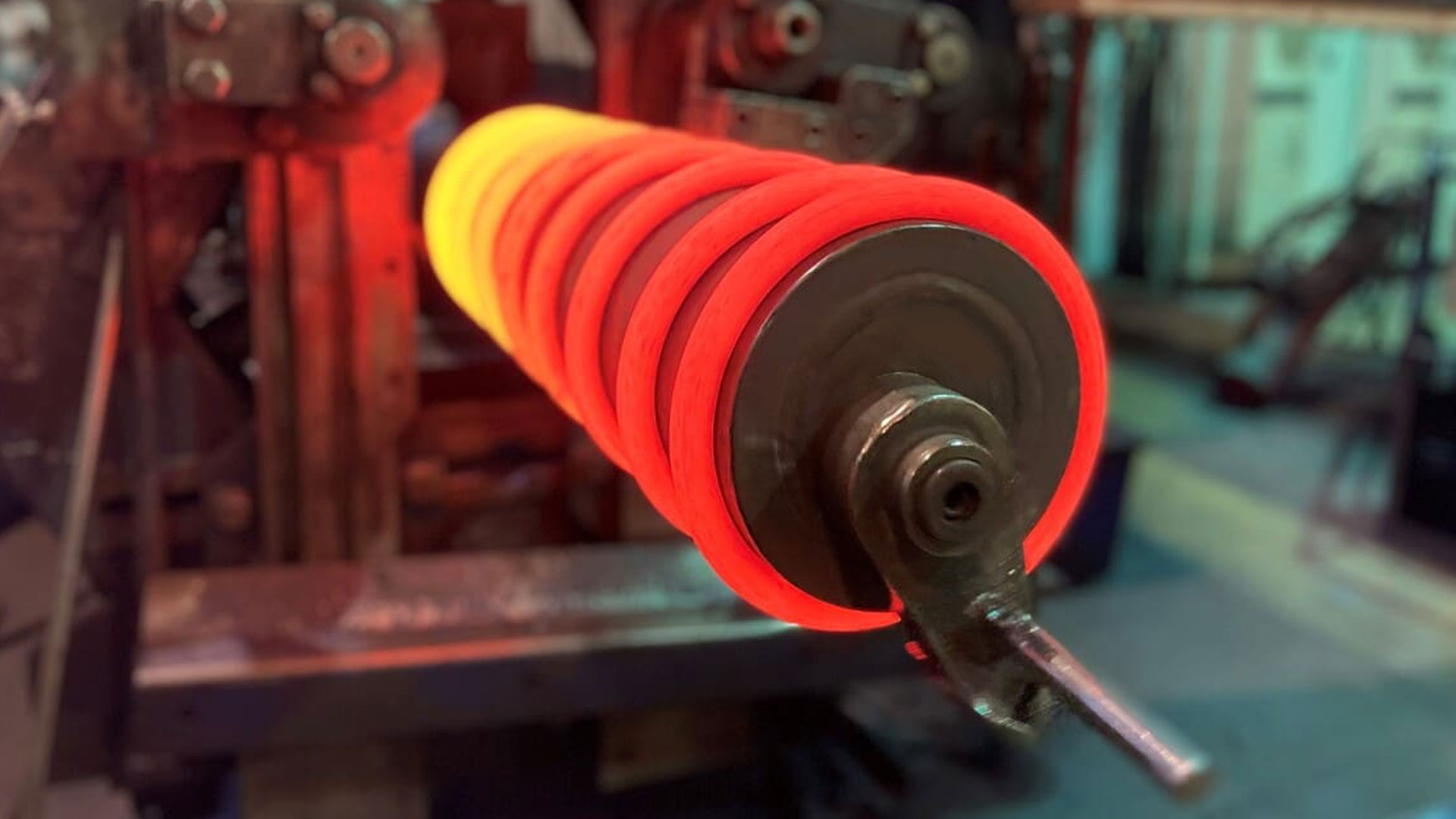
A hot coil spring is an elastic component that uses the force of elastic deformation to store energy. In the production process of hot coil springs, steel or other alloy materials need to be heated to high temperatures and then crimped and formed by specific processing methods to form the basic shape of the spring.
The manufacture and design of hot coil springs need to consider many factors, such as material properties, spring geometry,
load and deflection requirements.
The wire diameter of the hot-rolled spring is generally large; a hot coil spring’s wire diameter can reach 16-200mm and the
The production process adopts the hot-rolled approach. The manufacturer can shape the large spring as a right-hand or left-hand spring, cylindrical tension spring,

(Hot Coil Springs)
torsion spring, and conical, convex, or concave large spring.
Large springs easily twist and form after heating and have small resilience. After shaping, they need to be quenched and then tempered.
Based on the client’s requirements, the manufacturer will apply surface anti-rust treatment such as plastic spraying, spray painting, electroplating, or Dacromet.
Material: alloy spring steel: 60Si2MnA, 50CrVA, 4Cr13, 60Si2CrA,
Load capacity: 500N-10,000 N.
Hot coil spring with small wire diameters
Unlike small wire diameter springs, manufacturer can directly wound springs with small wire diameters, with spring steel wire when cold-rolled with greater resilience. Additionally, the manufacturer should consider the amount of spring back compensation in the winding tool and tempered instantly after coiling.
In breif, Hot coil springs and cold coil springs are two of the most common types of springs. And they differ in the manufacturing process and performance
characteristics:
Hot coil springs are made by processing steel or other alloy materials at high temperatures, usually between 300 and 600°C. During the heating process, the steel will undergo significant plastic deformation, making the
The spring has a higher elastic modulus and damping capacity. Hot coil springs are suitable for fields that require stable, heavy loads and frequent compressing, such as machinery, automobiles, aerospace, and other areas.
On the other hand, cold rolled springs are made at room temperature and do not require heating during processing. Cold-rolled springs are simpler and more cost-efficient to manufacture than hot-rolled springs. However, due to the small plastic deformation of the material, the elastic modulus and damping capacity of the cold rolled spring are relatively low, making it more suitable for occasions with a lighter load and small deformation requirements, such as electronics, instrumentation, and other fields.
In short, the manufacturing process and performance characteristics of hot and cold coil springs each have their benefits. And customers should choose the spring according to the specific application requirements.
Take a compression spring as an example:
The typical process of hot coil spring: Blanking— end conditioning (rolling flat or forging flat)— heating— coil spring—quenching—- Tempering — end face grinding — compression — (load test) — shot blasting (cleaning) — coating.
since Cold-rolled springs use materials that do not require heat treatment to roll, the process of a cold-rolled spring involves: rolling → stress relief annealing →, grinding of both ends → (shot blasting), (adjustment), (stress relief annealing) →, pressure test → inspection, →Surface anti-corrosion treatment.

This is effective and has helped me some