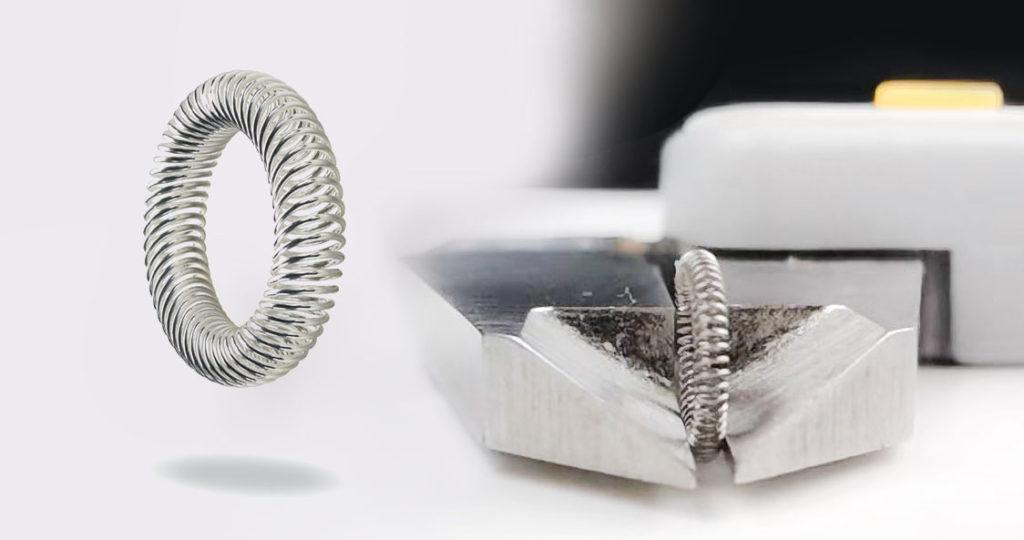
Facts and points about slant coil springs
What is a slant coil spring?
Canted coil springs, or spring fingers, finger springs, and touch springs, is a circular spring with elliptical and canted coils. When compressed each coil will deform independently. As a result, the spring reacts to every part of the coil when bend in a constant load on each contact point. Because canted coil spring can transmit strong currents in a small space and be used purely for mechanical connections. Therefore its use has no limits and is ideal for various static or dynamic medium high-pressure environments.
Due to the size of the spring fingers and the number of independent coils, the spring is more fit for various electrical contact designs and uses for electrical or EMI shielding with large contact current carrying capacity. Since each coil will separately react with contact and surface variations. Therefore, allows for a broader range of tolerances between fittings. In short, multiple contact points increase conductivity and operate at cooler temperatures for longer life.

(Electronic caliper table measurement)
How does canted coil spring function?
For connectors, the machine welds the ends of the spring to form a complete ring. The spring can be placed in the receptacle and plug designed inside the groove for specific insertion or extraction stress requirements on each standard coil size. When installing the lug into the groove, the canted coil of the spring deforms under continued spring stress, resulting in resistance until the coil mates with the track. Afterwards, the load of the spring coil and the design of the slot will then create a constant spring stress. So that a corresponding pull-out force is required to disconnect the two parts on the buckle of the micro connector. In conclusion, the canted coil spring has two key roles and can reduce the number of piece in the system.
Where are canted coil spring used for?
Canted coil springs provide a dual function as a mechanical connector and maintain an electrical circuit between the male and female connectors, minimizing RF interference and complicating the interconnection design for electronics. The simple, compact design brings new challenges to interconnect designs for military, factory, and commercial applications. The speed of circuits raises while the size of electronic components lowers. Therefore, the connector needs to process more signals at a higher rate in a smaller space or the number of contacts in a more compact area, and the size of the connector is also smaller. Its unique elastic force-deformation curve, the margin The compression range of the spring can reach up to 35%. Above all, the relatively stable elastic force reduces the wear caused by the temperature difference, tolerance, and other deviations, and each spring ring can function independently.
Various industries utilize finger spring in power contacts.For instance medical electronics, medical devices, and aerospace. Additionally, finger springs are also used in industries such as defense, energy, and vehicles.
The advantages of finger springs are as follows:
- Compared to a standard spring, the structure of a finger spring is more straightforward, with a smaller volume, requiring lesser material and a lower cost. Finger springs meet the meet of fitting in a small space in a device design. Futher more, they are fitting for compact design, and have a small number of components. Simplifying the creation of connecting devices.
- Multi-point contact, highly concentrated force, can achieve almost lossless connection. Guaranteeing serious current carrying capacity. Along with good electrical conductivity, and high electrical and thermal stability.
- The contact pressure of each contact point is low and has good wear resistance.
- The unique structure not only gives it a great working range, but also allow a large tolerance on the contact surface, and has greater adaptability to machining and assembly errors. Consequently, making it more fit for mass production.
The scope of application of finger springs:
- High and medium voltage switch
- High Current Connections
- Bus connector
- Embedded Pole
- High voltage electric chain end piece
- Fuse link Connections
- Mechatronic Applications

